Why Regularly Defragment Your Hard Drive on Windows XP
Among Windows' System Maintenance Tools, Disk Defragmenter is one of the easiest and most useful, and has a direct impact on your computer's performance. As time passes, files accumulate and files are deleted from your hard drive: this results in having files scattered in multiple places on your hard drive.  Defragmenting a drive on Windows will consolidate all valid files together, close to the center of the hard drive, making it faster to retrieve them. This is how defragmenting your drive usually "makes" Windows faster: it simply has less searching and retrieval work to perform once most files are close together.
Defragmenting a drive on Windows will consolidate all valid files together, close to the center of the hard drive, making it faster to retrieve them. This is how defragmenting your drive usually "makes" Windows faster: it simply has less searching and retrieval work to perform once most files are close together.
Launching Windows' Disk Defragmenter
 To start Microsoft Windows' Disk Defragmenter, click the Windows Start button, and go to Programs > Accessories > System Tools > Disk Defragmenter.
To start Microsoft Windows' Disk Defragmenter, click the Windows Start button, and go to Programs > Accessories > System Tools > Disk Defragmenter.
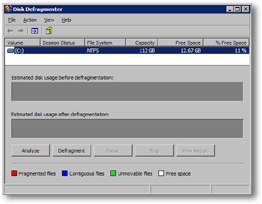 The Disk Defragmenter window will open, and show you a brief summary of all drives (internal or external) currently available to your computer.
The Disk Defragmenter window will open, and show you a brief summary of all drives (internal or external) currently available to your computer.
Note that Windows' Disk Defragmenter also includes partitions in its summary. Simply put, partitions are "virtual drives"; a single hard drive can have several partitions, each of which will be perceived and treated as a real hard drive.
Each of your hard drives, partitions, and external drives are assigned a letter: the default hard drive or partition is nearly always called "C:". Operating system (Windows) and programs run from it.
Launching Windows' Disk Defragmenter from the Local Disk Properties
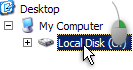 Another way to launch Windows' Disk Defragmenter is to open Windows Explorer (double-click on the My Computer icon on your Desktop). Locate the drive you would like to defragment, right-click on it, and choose Properties.
Another way to launch Windows' Disk Defragmenter is to open Windows Explorer (double-click on the My Computer icon on your Desktop). Locate the drive you would like to defragment, right-click on it, and choose Properties.
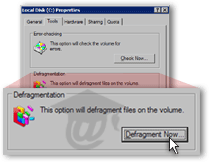 Select the Tools tab from the Local Disk (X:) Properties, (where X is the drive letter that has been assigned to the hard drive you wish to defragment, "C:" by default for the primary Windows drive or partition).
Select the Tools tab from the Local Disk (X:) Properties, (where X is the drive letter that has been assigned to the hard drive you wish to defragment, "C:" by default for the primary Windows drive or partition).
Under Defragmentation, click the Defragment Now button, and Windows' Disk Degragmenter window will open, and the drive you wanted to defragment should be automatically selected.
Click Defragment Now to launch the Windows Disk Defragmenter tool.
Analyzing a Drive with Windows' Disk Defragmenter
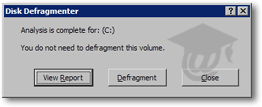 Under the Disk Defragmenter's listing of available drives, select the drive you would like to analyze and click the Analyze button. Depending on the size of drive and the speed of your computer's processor, this analysis will take anywhere from a few seconds to a few minutes, after which the Disk Defragmenter will display its verdict.
Under the Disk Defragmenter's listing of available drives, select the drive you would like to analyze and click the Analyze button. Depending on the size of drive and the speed of your computer's processor, this analysis will take anywhere from a few seconds to a few minutes, after which the Disk Defragmenter will display its verdict.
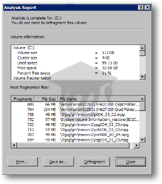 To view a detailed Disk Defragmentation report, click the View Report button; it will open the Analysis Report dialog, which contains a somewhat cryptic synopsis of your drive's shape.
To view a detailed Disk Defragmentation report, click the View Report button; it will open the Analysis Report dialog, which contains a somewhat cryptic synopsis of your drive's shape.
Aside from the Windows Disk Defragmenter's conclusion whether a defragmentation is warranted or not, the information that matters to you is located in the top portion of the Analysis Report: ideally, you should have 20% or more of free space available on Windows (see the percentage under Percent free space).
You can print your defragmentation report (click Print), save it as a text file (click Save As), start defragmenting the selected drive (Defragment button), or dismiss the dialog (Close).
Initiating the Hard Drive Defragmentation Process on Windows
To initiate the defragmentation process and optimize the distribution of data on your hard drive, click the Defragment button from the Disk Defragmenter window, or the Defragment button on the Analysis Report dialog.
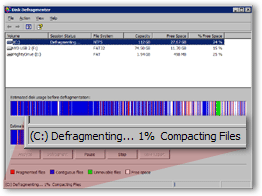 Depending on the speed of your computer's processor and the size of your hard drive, hard drive defragmentation is an resource intensive operation that typically requires a few hours.
Depending on the speed of your computer's processor and the size of your hard drive, hard drive defragmentation is an resource intensive operation that typically requires a few hours.
During this time, it is wiser not to use your PC.
To get an idea of the hard drive defragmentation progress, notice the text container on the bottom left, in the Disk Defragmenter's status bar. It gives you a real time update of the defragmentation process.
Note: this tutorial was created for Windows XP and previous versions of Windows; if you are using Windows Vista, defragmentation is automatically taken care of for you. Read our tutorials on Windows Vista maintenance and performance…