Change screen resolution in Windows XP
Your monitor (display) and graphics card determine together the supported "screen resolutions" at your disposal.  What Is Screen Resolution? - The physical size of your display is fixed (diagonal length measured in inches). The resolution is determined by software, and define the amount of pixels visible on screen. The higher the resolution, the more you see on your screen, but also the tinier it gets, since more image needs to fit on a fixed monitor size.
What Is Screen Resolution? - The physical size of your display is fixed (diagonal length measured in inches). The resolution is determined by software, and define the amount of pixels visible on screen. The higher the resolution, the more you see on your screen, but also the tinier it gets, since more image needs to fit on a fixed monitor size.
Changing Your Screen Resolution on Windows
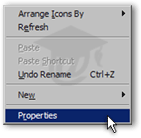
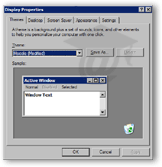 The easiest way to change your screen resolution on Windows is to right-click on an empty area of your desktop.
The easiest way to change your screen resolution on Windows is to right-click on an empty area of your desktop.
From the context menu that appears, click Properties, which should be the last item displayed on the menu.
Windows' Display Properties window will open, with the first tab selected.
Testing Different Screen Resolutions on Windows
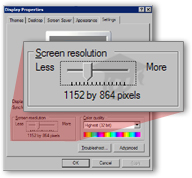 Click the Display Properties' Settings tab, normally the rightmost tab.
Click the Display Properties' Settings tab, normally the rightmost tab.
Under the Settings tab, locate the horizontal slider, under the Screen Resolution (or "Screen Area", depending on your Windows version).
Move the slider to the right (higher screen resolution) or left (smaller screen resolution) to adjust your screen resolution.
Remember: high screen resolution means that you see more things, but tinier. At a smaller screen resolution, you see less things at once, but larger images.
Windows' Display Properties window should only display screen resolutions that are supported by your monitor (display) and your graphics card (the piece of hardware that allows the computer and the monitor to interact).
 Depending on your Windows settings and your Windows version, the screen resolution change will take effect immediately, after a short delay, or after restarting Windows. Click the Apply button to preview the new screen resolution. Notice that as you move the slider, Windows gives you a preview of the new screen resolution inside the monitor image.
Depending on your Windows settings and your Windows version, the screen resolution change will take effect immediately, after a short delay, or after restarting Windows. Click the Apply button to preview the new screen resolution. Notice that as you move the slider, Windows gives you a preview of the new screen resolution inside the monitor image.